Apple Watch or Oxygen Monitor?

The Apple Watch Series 7,continues to include an ECG for monitoring heart health as well as a blood oxygen monitor. While the existing ECG did receive FDA clearance, the blood oxygen monitor did not. It has raised some questions after its launch:
·How accurate or useful (or revolutionary) is that blood oxygen feature?
·Can the future of health really be on our wrist?
Health experts say while the data collected from wearable devices is helpful for both patients and doctors, they are not a replacement for medical-grade devices.
Low blood oxygen levels, or hypoxemia, have been linked to COVID-19 because the disease affects your ability to get enough oxygen. Doctors have used SpO2 levels to determine the severity of COVID-19 cases and treat those patients accordingly. But hypoxemia can be caused by many other heart and lung issues, such as asthma, pneumonia, and congenital heart disease.
What Is the Accuracy?
Apple’s marketing release tells us that their blood oxygen sensor “employs four clusters of green, red, and infrared LEDs, along with the four photodiodes on the back crystal of Apple Watch, to measure light reflected back from blood. Apple Watch then uses an advanced custom algorithm built into the Blood Oxygen app, which is designed to measure blood oxygen between 70 percent and 100 percent.”Apple is marketing this as a wellness feature rather than for medical monitoring.
Although we don’t know for sure about AW7’s accuracy, we do have studies showing us that reflectance oximetry (used in AW7) is not as accurate or stable as transmittance oximetry (used in fingertip pulse oximeters.) It’s important to understand this significant technological difference.
Since Apple was marketing the ECG as a tool for monitoring health conditions, the company had to prove it worked for its intended purpose.
“While these devices can help provide patients with a general trend regarding their health, the data should not be used to provide medical care or trigger medical interventions,” said Dwivedi, assistant professor at Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra and cardiologist at Northwell Health.
How Does Blood Oxygen Monitor Work?
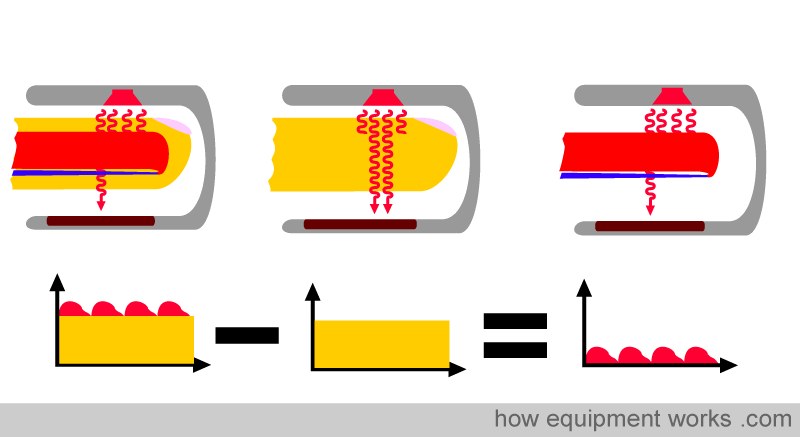
Oximeters determine oxygen saturation (SpO2) in tissues by quantifying the concentration of hemoglobin bound to oxygen (oxyhemoglobin or HbO2) and hemoglobin (Hb) without oxygen. Pulse oximeters, which are widely utilized in medical settings, utilize photoplethysmography (PPG) performed on pulsatile arterial blood at two different wavelengths to obtain a ratio of HbO2 and Hb. Optoelectronic sensors composed of light-emitting diodes and photodiodes that operate at red and near-infrared wavelengths capitalize on the differing absorptivity of Hb and HbO2.
Transmission-mode oximetry has been the gold standard but requires sensing at tissue locations that can be transilluminated with the light shining through the tissue such as the earlobes and fingers.
With reflective mode oximetry, the light sources and photodiodes are on the same side of the tissue and a thin measurement site is not required. Thus, it can be used at measurement sites such as the forehead, chest, and (most relevant for this discussion) the wrist, where a band or watch can be utilized.
Reflectance mode oximetry, the model utilized by Apple Watch, has been shown to be inferior to the transmission mode used by fingertip pulse oximeters, likely due to increased variability introduced by ambient light, the pressure applied, and positional variation inherent to the method.
Some smartphone apps have claimed an ability to measure SpO2 using reflectance, but when two were studied they were found to be seriously inaccurate. Walter Schrader, MD, who co-authored the smartphone oximetry study, has told that he does not recommend any smartphone app as a reliable pulse oximeter.
Should You Buy Apple Watch for Medical Use?
We can assert that the wrist technique is generally less accurate than the typical technique of measuring blood oxygen using a finger sensor.
If you are primarily excited by the blood oxygen sensing capabilities of AW, I would recommend instead purchasing an oximeter. At least we have some data on these devices, which use the more reliable transmission mode for measuring oxygen saturation. Anthony C. Pearson, MD, a noninvasive cardiologist, and professor of medicine at St. Louis University School of Medicine.
Shop our Oxygen Monitor Range here.
