Basic Facts About EKG/ECG Monitor That You Don't Know
Many people have heard or had an EKG (electrocardiogram) done in their life, whether in a hospital or cardiology clinic, the electrocardiogram is a routine examination. Both ECG and EKG refer to the same procedure, while ECG is shortened from the English spelling of electrocardiogram and EKG is derived from German elektrokardiogramm.
Though familiar with the term EKG, most people know little about it. One of my friends even told me, “When doing EKG test, I worry about getting an electrical shock! Every time when I am going to do a 12-lead EKG, I feel nervous.” Actually, EKG is a safe, non-invasive, painless test and has no major risks.
As EKG is the most common physical examination, there are some basic facts that you have to know, so that you will not be nervous when doing the EKG test, or feel confused after reading the EKG results.
What does an EKG monitor do to your heart?
An EKG monitor is used to record the heart’s own electrical activity.
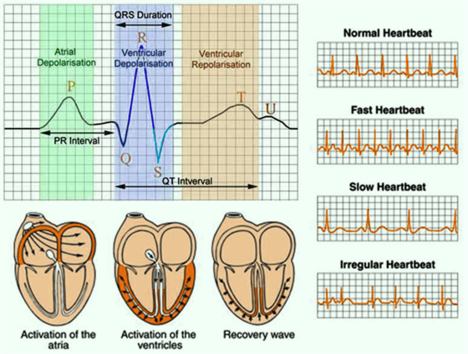
The beating of the heart is directed by its own electrical signals. The electrocardiogram machine can record these signals and show them through curves.
If there is a problem with the heart, the electrical signal of the heart will be abnormal, and the EKG waveform will be different. Through the EKG waveform, doctors can see if there is a problem with the patient’s heart.
EKG tests do not cause any damage to the heart. It’s just a recording device, so you don’t have to be nervous when you’re doing an EKG.
Is it necessary to make EKG a part of a routine physical exam?
Commonly, many institutions take EKG as a routine physical exam. EKG tests are always used to screen heart disease.
These people below must do the electrocardiogram test:
• Persons over 60 years of age;
• People with risk factors of cardiovascular disease such as hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipidemia;
• Regular smokers.
The risk of heart disease in these groups of people is much higher than in others. So it is necessary to carry out EKG examinations regularly.
EKG Results
The electrical signal of the heart is very complicated. It is difficult for people who are not cardiologists to thoroughly understand the EKG. So it is best to consult a cardiologist to interpret the EKG if you are in doubt about the EKG results.
In general, words in EKG reports like “sinus rhythm” and “sinus arrhythmia” mean a relatively normal situation.
There are abnormal EKG examples like “conduction block” “myocardial infarction” “tachycardia” “bradycardia”. If you experience those EKG events, you need to go to seek emergency medical attention.
What does the words “sinus rhythm” of an EKG report mean?
Some EKG reports have a lot of confusing technical terms.
For example, in many reports, the first sentence is “sinus rhythm”. Many people don’t know what it means.
As a matter of fact, “sinus rhythm” is the signal of heartbeats. “Sinus” refers to an anatomical structure of the heart called the sinoatrial node.
The heart must start beating from the sinoatrial node, or it is an abnormality or disease.
Other Cardiac Tests
Some friends have the experience: the heart is uncomfortable, but the EKG result is normal. Why is that?
The electrocardiogram is a tool to analyze the electrical activity of the heart, but it only reflects one aspect of the heart.
There is a metaphor circulating among doctors that vividly explains the function of various cardiac tests as here:
If you think of the heart as a house,
• The echocardiogram is used to see how many rooms the house has, and if the wall of the house is good;
• The electrocardiogram is used to see whether the circuit is normal;
• The coronary angiogram is used to see if the pipes in the house are blocked or leaking.
We can see that only when the abnormal electrical activities of the heart occur, the electrocardiogram will be abnormal.
Several reasons why your heart feels uncomfortable but your ECG is fine
1. The monitoring time is not enough
People may be only hooked up to the machine for a very brief amount of time, so heart rhythm irregularities are not shown in the EKG waveform. Thus the doctor will suggest the patient continuously monitor their hearts for over 24 hours.
2. It’s not a heart problem
“Heart is not comfortable” is a very subjective feeling. Having this feeling does not necessarily mean heart problems. It may be temporary emotional distress or stomach disease. The stomach and heart are close together, so it’s easy to get confused. Sometimes the doctor will also ask patients with stomachache to do an electrocardiogram.
3. It’s too mild
When the heart abnormality is so mild that it is not recognized by an EKG, other tests may be needed.
4. It’s too severe
Sometimes heart disease is so serious that the electrocardiogram judgment is “false negatives” (where the test fails to identify a real problem), which is related to the principle of the electrocardiogram. Doctors will make a comprehensive judgment based on the patient’s physical condition, and the results of the ultrasound, chest X-ray, and other heart examinations.